Shih-Min Hsia
Taipei Medical University, Taiwan
Title: The effect of fucoidan on proliferation of leiomyoma cell
Biography
Biography: Shih-Min Hsia
Abstract
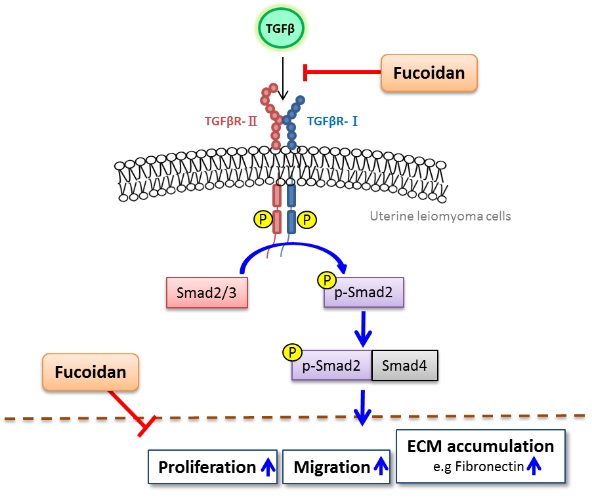
Statement of the Problem: Uterine leiomyoma (UL) are benign uterine tumors and the most notable pathophysiologic feature is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM). Fucoidan is a polysaccharide extracted from brown seaweeds, possesses a wide range of pharmacological properties, such as anti-tumor, anti-thrombotic, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effect. The aim was to study the effect of fucoidan on the growth of UL activated by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β).
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: ELT-3 uterine fibroids cells viability was determined by MTT method, cell cycle and cell apoptosis were stained with PI only or annexin V-FITC and PI, expressions of TβR-I, TβR-II, p-Smad2, Smad2/3, and fibronectin proteins was assayed by Western blot assay, cellular migration was assayed by wound healing assay, localizations of fibronectin were assayed by immunofluorescence analyses in each treatment group.
Findings: Treated ELT-3 cell with 0.5-2 mg/mL fucoidan from the brown alga Saccharina cichorioides and observed that fucoidan caused 50% growth inhibition with the high dose of 2 mg/ml after 48 h. Fucoidan induces sub-G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Fucoidan down-regulated TβR-II, p-Smad2 protein levels and significantly inhibits migration and fibronectin localization in TGF-β1-induced ELT-3 cells.
Conclusion & Significance: Fucoidan displays anti-proliferation, anti-fibrotic effects and exerts protective effects against the UL development.